Usage with docker
Requirements
Schema
Stacks management
- Stacks are managed with docker compose (
docker compose up -d) - Stacks can be stopped/downed without loosing data as named volumes are used for persistence (use
docker compose down --volumesto explicitly delete volumes)
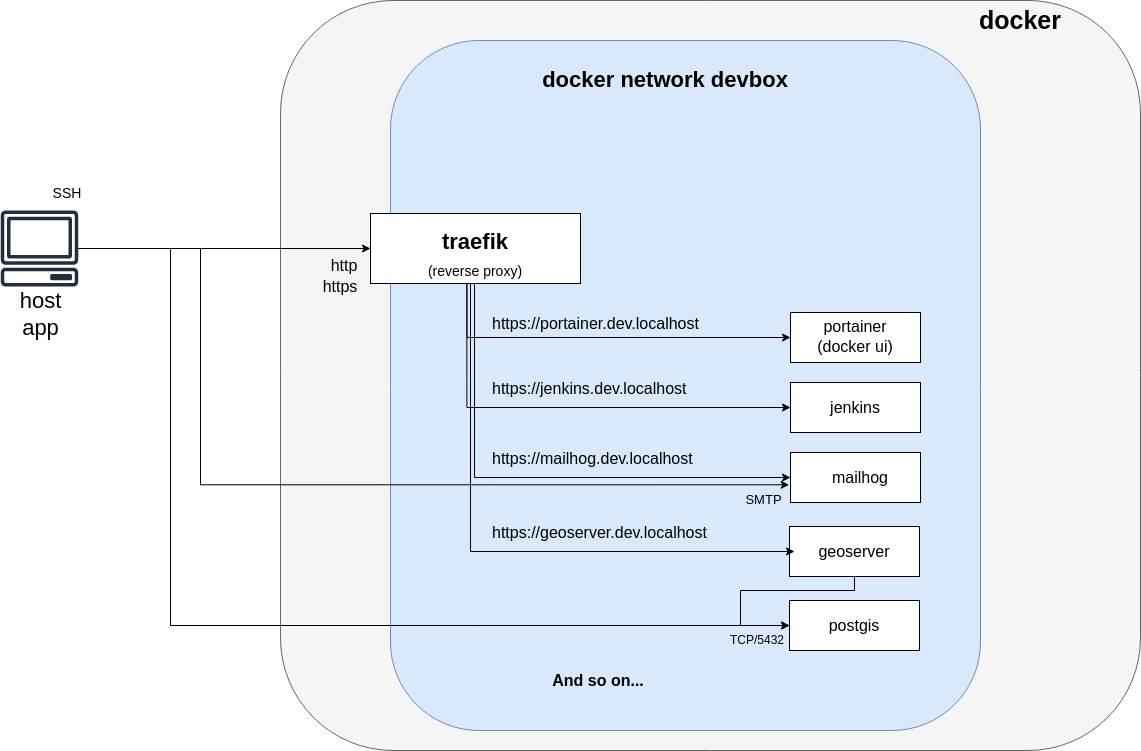
Networking and service exposition
- Applications are exposed on nice URL (ex : https://whoami.dev.localhost) with the reverse proxy traefik.
- An environment variable
DEVBOX_HOSTNAMEallows to customizedev.localhost - An helper script is provided to generate wildcard certificates for traefik with mkcert a wildcard certificate (traefik/mkcert/generate.sh).
- All stacks runs on the same network named
devboxto simplify communication between containers/stacks.
dev.localhostis preferred tolocalhostas it allows wildcard certificate generation.
Port mapping
By default, service ports (ex : 5342 for PostgreSQL) are only exposed on 127.0.0.1 for security consideration :
- My IDP enables IPV6 with no descent firewall.
- Docker overwrites
iptablesor UFW rules (so that is not trivial to configure a local firewall).
Note that you can overwrite this behavior by defining DEVBOX_PORT_PREFIX before starting stacks :
export DEVBOX_PORT_PREFIX=""
cd redis
docker compose up -d
Docker configuration
-
Ensure that you have a correct docker daemon configuration (
/etc/docker/daemon.json) :- Configure
bipanddefault-address-poolsto avoid IP overlaps on your LAN - Configure
storage-driverto “overlay2” - …
- Configure
-
You may have a look at least to docker-bench-security to avoid main security issues.
Docker networking and Traefik
To ease IP whitelisting and avoid the requirement to share the same network between traefik and exposed containers, note that traefik can be installed as a systemd service.
An alternative consists in using network_mode: 'host' on traefik/compose.yaml.
In both cases :
- traefik will see real client ip
- traefik will be able to forward to any container
Note that :
- The main limitation is that you may face problem using middlewares like thomseddon/traefik-forward-auth (when
http://traefik-forward-auth:4181is referenced in a middleware, docker internal DNS doesn’t seams to be invoked to resolvetraefik-forward-auth) - Kubernetes solves this issue with a different networking approach (by default, “A Pod can communicate with another Pod by directly addressing its IP address” without an explicit network sharing)
Resources
docs.docker.com - Reference documentation :
- docs.docker.com / Docker CLI (docker) for
docker ...commands - docs.docker.com / Docker CLI (docker) / docker compose for
docker compose...commands - docs.docker.com / Docker CLI (docker) / docker context to use a remote daemon engine through SSH for example.
- …
Ansible playbooks :
- mborne/ansible-docker-ce to install docker community engine with Ansible and configure it according to docker-bench-security recommandations (Warning: Don’t use this one at IGNF, contact me)
- mborne/ansible-traefik to deploy traefik as systemd service with Ansible.